Principia Complexica
Mathematical and Computation Roots
-
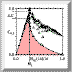
Crutchfield's computational
mechanics
-
Advantages
-
Based on computational understanding (mathematical logic, theory of computation)
-
Provides the notion of the edge-of-chaos
-
Uses statistical measures (We can make measurements)
-
Shows the way to representing the informational processes underlying Quantum
Mechanics
-
Lucidates the relationship between information and statistical mechanics
-
Disadvantages
-
Uses statistical measures (e.g., cannot blunt Prigogine's and Rosen's arguments
against reductionism)
-
Limited functional abstraction
-
Does not explicitly address the problem of Quantum Mechanics
-
Bohm's
ontological quantum theory
-
Advantages
-
Alternative to Quantum Mechanics: explains quantum effects
-
Clearly makes sense in the physical sense, gives you reason to hope that
we can find something about what underlies the quantum level
-
Disadvantages
-
Limited abstraction
-
No notion of complexity
-
Category Theory (John Baez
Robert
Rosen)
-
Advantages
-
Functions of Functions: Functors (Processes of Processes)
-
Abstraction/Generalization of Process Structure
-
Mathematical approach to go beyond reductionism
-
Disadvantages
-
No computational constructs
-
Obtuse
-
Fontana's compositional
dynamics
-
Advantages
-
Based on proof theory and lambda calculus, models of computation
-
Has symbolic notion of composition and decomposition
-
Lucidates the notion of organization
-
Disadvantages
-
Limited abstraction of process structure?
-
Limited notion of levels of complexity
-
Prigogine's
Laws of Chaos
-
Advantages
-
Based on dynamics, the foundation of physics
-
Has functional composition and decomposition
-
Functional analysis of coupling and decoupling (Poincaire resonances)
-
Lucidates time, irreversibilty, entropy and how to get order out of chaos.
-
Disadvantages
-
Limited abstraction
-
Limited information/computational representation
-
Limited notions of levels of complexity
Conceptual Roots
-
The edge-of-chaos region
-
Langton (phase transition - life)
-
Crutchfield, Mitchell (physical computation)
-
Kaufmann (autocatalysis)
-
Braeiss (optimal capacity of network)
-
Levels of Complexity
-
David West Keirsey (what is the context?)
-
Langton (edge of chaos)
-
Hegel (three - thesis (chaos), antithesis (order), synthesis (edge of chaos))
-
Quantum Replication
-
Why big bang
-
Crutchfield (physical computation)
-
Functional Shift
-
Adam Smith, Darwin (function, form)
-
Gould (pre-adaptation, punctuated equilibrium)
-
Prigogine (Poincaire's resonances)
-
Rosen (functional composition, decomposition)
-
Levels of Selection Process
-
Leo Buss (levels of selection)
-
Prigogine (chemistry selection)
-
Smolin (physical selection)
-
Maynard-Smith (linear encoding)
Keirsey's Comparative Complexity
-
Advantages
-
Disadvantages
-
No precise mathematics or computational models, except vague combination
of work of above
-
Underlying process still unexpressed (random vacuum, replication of quantum
information, encoding of information in rest mass and charge)
-
No clear representation of processes of processes.
-
Methodology of analysis requires understanding all levels of complexity.
Assumptions
-
Meta-Universe composed of random communication "states" (but non-State,
because they don't contain invariant information)
-
Rest "Mass" has some type of invariant information, but is encoded as part
of a process.
-
The invariant information in "Mass" encodes information for communication
and can be transmitted
-
The creation of "mass" is some type of "replication" process, the replication
process is also encoded as part of the State.
-
There is no absolute space, all states are relational and depend on process.
-
The relationship between State and energy(in space-time) is constant.
-
Invariant information is increasing in our universe
Definitions
State The information content of physical
existence. (a pattern of existence: reality)
state (a physical bit -- a physical difference
(0 or 1)) in the our world or meta-universe
You can think of our universe as being created by the infection of a
"reality virus" A set of random bits of information that happen to
encode replication of itself in a random sea of state: energy. This replication
spreads and replaces randomness (chaos) with unfolding order.
Massive Replicative/Dissipative
Structures
|